numpy.random.standard_cauchy#
- random.standard_cauchy(size=None)#
從標準柯西分佈(眾數 = 0)中抽取樣本。
也稱為勞倫茲分佈。
注意
新程式碼應使用
standard_cauchy方法,此方法屬於Generator實例;請參閱快速入門。- 參數:
- sizeint 或 int 元組,選填
輸出形狀。如果給定的形狀是,例如
(m, n, k),則會抽取m * n * k個樣本。預設值為 None,在這種情況下會傳回單一值。
- 返回:
- samplesndarray 或純量
抽取的樣本。
參見
random.Generator.standard_cauchy新程式碼應使用的方法。
註解
完整柯西分佈的機率密度函數為
\[P(x; x_0, \gamma) = \frac{1}{\pi \gamma \bigl[ 1+ (\frac{x-x_0}{\gamma})^2 \bigr] }\]標準柯西分佈僅設定 \(x_0=0\) 和 \(\gamma=1\)
柯西分佈出現在驅動諧波振盪器問題的解中,也描述了光譜線展寬。它也描述了以隨機角度傾斜的線切割 x 軸的值分佈。
當研究假設檢定(假設常態性)時,觀察檢定在來自柯西分佈的資料上的表現,是衡量它們對重尾分佈敏感度的好指標,因為柯西分佈看起來很像高斯分佈,但具有更重的尾部。
參考文獻
[1]NIST/SEMATECH 電子手冊統計方法,「柯西分佈」,https://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3663.htm
[2]Weisstein, Eric W. 「柯西分佈。」來自 MathWorld–Wolfram 網路資源。https://mathworld.wolfram.com/CauchyDistribution.html
[3]維基百科,「柯西分佈」 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cauchy_distribution
範例
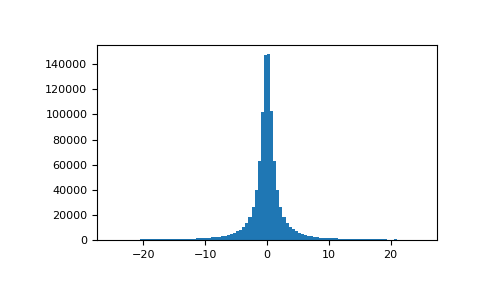
繪製樣本並繪製分佈圖
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> s = np.random.standard_cauchy(1000000) >>> s = s[(s>-25) & (s<25)] # truncate distribution so it plots well >>> plt.hist(s, bins=100) >>> plt.show()