numpy.logspace#
- numpy.logspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, base=10.0, dtype=None, axis=0)[原始碼]#
傳回在對數尺度上均勻間隔的數字。
在線性空間中,序列起始於
base ** start(以 base 為底的 start 次方),並結束於base ** stop(見下方的 endpoint)。在 1.25.0 版本變更: 現在支援非純量 ‘base`
- 參數:
- startarray_like
base ** start是序列的起始值。- stoparray_like
base ** stop是序列的最終值,除非 endpoint 為 False。在這種情況下,num + 1個值會在對數空間的區間上均勻間隔,其中除了最後一個值以外的所有值 (長度為 num 的序列) 都會傳回。- numinteger, optional
要產生的樣本數。預設值為 50。
- endpointboolean, optional
若為 true,stop 是最後一個樣本。否則,它不會被包含在內。預設值為 True。
- basearray_like, optional
對數空間的底數。在
ln(samples) / ln(base)(或log_base(samples)) 中元素之間的步長是均勻的。預設值為 10.0。- dtypedtype
輸出陣列的型別。若未給定
dtype,則資料型別會從 start 和 stop 推斷而來。推斷的型別永遠不會是整數;即使引數會產生整數陣列,也會選擇 float。- axisint, optional
結果中儲存樣本的軸。僅在 start、stop 或 base 為類陣列時相關。預設情況下 (0),樣本將沿著在開頭插入的新軸排列。使用 -1 可在結尾取得軸。
- 傳回值:
- samplesndarray
num 個樣本,在對數尺度上均勻間隔。
另請參閱
arange類似於 linspace,但指定步長而非樣本數。請注意,當與浮點數 endpoint 一起使用時,endpoint 可能會也可能不會被包含在內。
linspace類似於 logspace,但樣本在線性空間中均勻分佈,而不是在對數空間中。
geomspace類似於 logspace,但直接指定端點。
- 如何建立具有規律間隔值的陣列
註解
如果 base 是純量,則 logspace 等同於以下程式碼
>>> y = np.linspace(start, stop, num=num, endpoint=endpoint) ... >>> power(base, y).astype(dtype) ...
範例
>>> import numpy as np >>> np.logspace(2.0, 3.0, num=4) array([ 100. , 215.443469 , 464.15888336, 1000. ]) >>> np.logspace(2.0, 3.0, num=4, endpoint=False) array([100. , 177.827941 , 316.22776602, 562.34132519]) >>> np.logspace(2.0, 3.0, num=4, base=2.0) array([4. , 5.0396842 , 6.34960421, 8. ]) >>> np.logspace(2.0, 3.0, num=4, base=[2.0, 3.0], axis=-1) array([[ 4. , 5.0396842 , 6.34960421, 8. ], [ 9. , 12.98024613, 18.72075441, 27. ]])
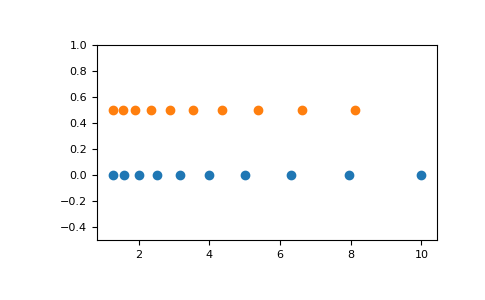
圖形化說明
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> N = 10 >>> x1 = np.logspace(0.1, 1, N, endpoint=True) >>> x2 = np.logspace(0.1, 1, N, endpoint=False) >>> y = np.zeros(N) >>> plt.plot(x1, y, 'o') [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>] >>> plt.plot(x2, y + 0.5, 'o') [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>] >>> plt.ylim([-0.5, 1]) (-0.5, 1) >>> plt.show()