numpy.histogram2d#
- numpy.histogram2d(x, y, bins=10, range=None, density=None, weights=None)[原始碼]#
計算兩個資料樣本的二維直方圖。
- 參數:
- xarray_like,形狀為 (N,)
一個包含要繪製直方圖的點的 x 座標的陣列。
- yarray_like,形狀為 (N,)
一個包含要繪製直方圖的點的 y 座標的陣列。
- binsint 或 array_like 或 [int, int] 或 [array, array],可選
bin 的規格
如果為 int,則為兩個維度的 bin 數量 (nx=ny=bins)。
如果為 array_like,則為兩個維度的 bin 邊緣 (x_edges=y_edges=bins)。
如果為 [int, int],則為每個維度的 bin 數量 (nx, ny = bins)。
如果為 [array, array],則為每個維度的 bin 邊緣 (x_edges, y_edges = bins)。
組合 [int, array] 或 [array, int],其中 int 是 bin 的數量,而 array 是 bin 邊緣。
- rangearray_like,形狀為 (2,2),可選
沿每個維度的 bin 的最左邊和最右邊邊緣(如果未在 bins 參數中明確指定):
[[xmin, xmax], [ymin, ymax]]。此範圍之外的所有值都將被視為離群值,並且不會在直方圖中計數。- densitybool,可選
如果為 False(預設值),則傳回每個 bin 中的樣本數。如果為 True,則傳回 bin 的機率密度函數,
bin_count / sample_count / bin_area。- weightsarray_like,形狀為 (N,),可選
一個值為
w_i的陣列,用於權衡每個樣本(x_i, y_i)。如果 density 為 True,則權重會正規化為 1。如果 density 為 False,則傳回的直方圖的值等於屬於落入每個 bin 的樣本的權重總和。
- 傳回值:
- Hndarray,形狀為 (nx, ny)
樣本 x 和 y 的二維直方圖。x 中的值沿第一個維度繪製直方圖,而 y 中的值沿第二個維度繪製直方圖。
- xedgesndarray,形狀為 (nx+1,)
沿第一個維度的 bin 邊緣。
- yedgesndarray,形狀為 (ny+1,)
沿第二個維度的 bin 邊緣。
另請參閱
histogram一維直方圖
histogramdd多維直方圖
註解
當 density 為 True 時,傳回的直方圖是樣本密度,定義為 bin 值的總和與 bin 面積的乘積
bin_value * bin_area為 1。請注意,直方圖不遵循笛卡爾坐標慣例,其中 x 值在橫坐標上,而 y 值在縱坐標軸上。相反地,x 沿陣列的第一個維度(垂直)繪製直方圖,而 y 沿陣列的第二個維度(水平)繪製直方圖。這確保與
histogramdd的相容性。範例
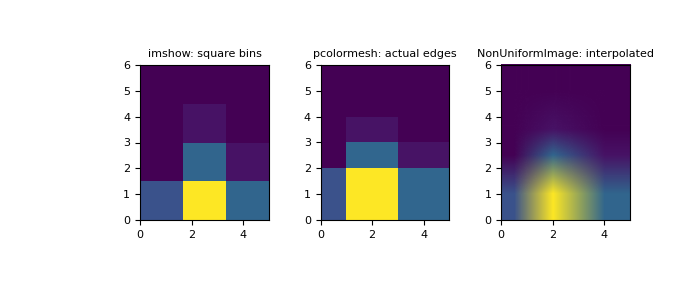
>>> import numpy as np >>> from matplotlib.image import NonUniformImage >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
建構具有可變 bin 寬度的二維直方圖。首先定義 bin 邊緣
>>> xedges = [0, 1, 3, 5] >>> yedges = [0, 2, 3, 4, 6]
接下來,我們建立一個具有隨機 bin 內容的直方圖 H
>>> x = np.random.normal(2, 1, 100) >>> y = np.random.normal(1, 1, 100) >>> H, xedges, yedges = np.histogram2d(x, y, bins=(xedges, yedges)) >>> # Histogram does not follow Cartesian convention (see Notes), >>> # therefore transpose H for visualization purposes. >>> H = H.T
imshow只能顯示方形 bin>>> fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 3)) >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(131, title='imshow: square bins') >>> plt.imshow(H, interpolation='nearest', origin='lower', ... extent=[xedges[0], xedges[-1], yedges[0], yedges[-1]]) <matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x...>
pcolormesh可以顯示實際邊緣>>> ax = fig.add_subplot(132, title='pcolormesh: actual edges', ... aspect='equal') >>> X, Y = np.meshgrid(xedges, yedges) >>> ax.pcolormesh(X, Y, H) <matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x...>
NonUniformImage可以用於顯示具有內插的實際 bin 邊緣>>> ax = fig.add_subplot(133, title='NonUniformImage: interpolated', ... aspect='equal', xlim=xedges[[0, -1]], ylim=yedges[[0, -1]]) >>> im = NonUniformImage(ax, interpolation='bilinear') >>> xcenters = (xedges[:-1] + xedges[1:]) / 2 >>> ycenters = (yedges[:-1] + yedges[1:]) / 2 >>> im.set_data(xcenters, ycenters, H) >>> ax.add_image(im) >>> plt.show()
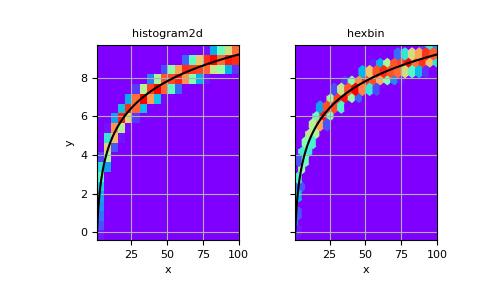
也可以建構不指定 bin 邊緣的二維直方圖
>>> # Generate non-symmetric test data >>> n = 10000 >>> x = np.linspace(1, 100, n) >>> y = 2*np.log(x) + np.random.rand(n) - 0.5 >>> # Compute 2d histogram. Note the order of x/y and xedges/yedges >>> H, yedges, xedges = np.histogram2d(y, x, bins=20)
現在,我們可以使用
pcolormesh繪製直方圖,並使用hexbin進行比較。>>> # Plot histogram using pcolormesh >>> fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, sharey=True) >>> ax1.pcolormesh(xedges, yedges, H, cmap='rainbow') >>> ax1.plot(x, 2*np.log(x), 'k-') >>> ax1.set_xlim(x.min(), x.max()) >>> ax1.set_ylim(y.min(), y.max()) >>> ax1.set_xlabel('x') >>> ax1.set_ylabel('y') >>> ax1.set_title('histogram2d') >>> ax1.grid()
>>> # Create hexbin plot for comparison >>> ax2.hexbin(x, y, gridsize=20, cmap='rainbow') >>> ax2.plot(x, 2*np.log(x), 'k-') >>> ax2.set_title('hexbin') >>> ax2.set_xlim(x.min(), x.max()) >>> ax2.set_xlabel('x') >>> ax2.grid()
>>> plt.show()